
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.
1, detect the serial line is good or bad
1) Plug the serial cable into the computer and short-circuit the 2 and 3 pins of the serial port
2) Open the serial debugging assistant
3) Click Auto-send, send a random data in the automatically sent window to see if it can receive the self-transmitted data that the serial line is normal, otherwise it is bad.
2, after the completion of the microcontroller program, take a look at the serial port for data detection
3, the meaning of the 4 lights that the module communicates with the module on the one-chip computer
1)DO lamp
Flashing indicates that the serial port of the SCM serial port and the GSM module are not communicating properly, otherwise the serial port communication is normal.
2) D1 light
The light indicates that the module is registered on the network, otherwise it is not registered on the network
3) D2 light
Lights up to start texting
4) D3 light
Lights up to end the text message
4. Connection of MCU board and GSM module
SCM ---------GSM module
VCC--------vcc (pin 3 of P5)
GND--------GND (pin 4 of P5)
RX_232 (indicating the sending of the SCM)----------RXDPC_232 (receiving of the module (pin 5 of P5))
TX_232 (represents the receipt of the SCM) ---------- TXD_PC232 (Send of the module (P5 pin 6))
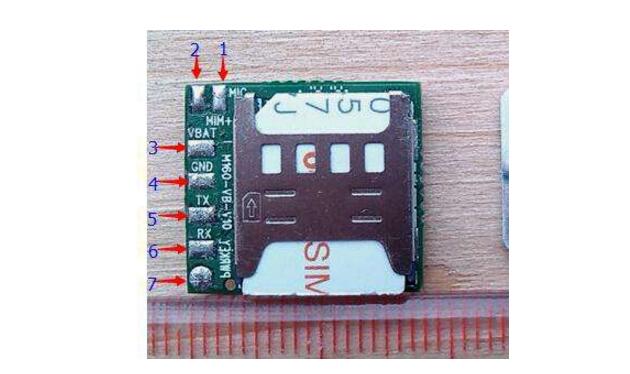
One-chip computer connects GSM module, can connect TX and RX of asynchronous serial communication port directly, do not forget the ground wire.
Precautions:
1. Different MCUs have different voltages. The input and output levels of the general GSM module are 2.85V, and the level of the 51 series is 5V. Generally, the resistance of the 2K series connected to the 51 output TX line can basically be used. If it is a 3.3V microcontroller, this resistance can be very small, a few hundred ohms can be.
2. The power supply of the GSM module and the SIM card circuit are very troublesome. First of all, most of the GSM modules use the interface of the FPC40. The distance between the cables is only 0.5mm, and it is a plastic case, which is not good for welding. If welding is not good, work is unstable. Followed by the more troublesome power supply, GSM module emission current is larger, the maximum instantaneous current 2A! Therefore, the power supply part generally uses a high-current DC-DC converter such as the LM2576 to provide a voltage of 4V. The design of the DCDC circuit itself is not easy, and it is difficult for a personal application to require a circuit board. Latency of instability. There is also a SIM card. The communication between the SIM card and the GSM module itself is a complicated high-frequency process. The circuit has strong anti-interference ability. I once tried to connect them with wires and dropped them in ten minutes. Therefore, the SIM card part needs to be carefully designed. Do not look at only five data lines.
MCU control TC35GSM module method 1, hardware connectionThe circuit shown in the figure below only needs to design a TTL-to-RS232 level circuit, which is connected to the UART port of the MCU, and the other end is directly connected to the TC35.

The serial port of the one-chip computer sets up mode 1 (9600, N, 8, 1), export AT+xxx to UART port in ASCII code form sequentially ; The data of receiving TC35 adopts and cuts off the way. A detailed list of procedures (Keil C51) is given here, but the programming method is not described. The procedure is as follows:
// Definition of AT command
Char code AT_Tc35[]=“AT+”; //Consecutive
Char code Bps_Tc35[]=“IPR=38400”; //Baud rate
Char code Text_Tc35[]="CMGF=1"; //text mode
Char code Read_Tc35[]=“CMGR=”; //Read information
Char code Erase_Tc35[]=“CMGD=”; //Delete message
Char code Send_Tc35[]=“CMGS=”; //Send message
Char code Creg_Tc35[]=“CREG?”; //Register
//Mode setting
Void UART_Init(void)
{
SCON=0x50; //01010000b=”1 pattern scon,#11011000b;
ES=l;
}
// send - ASCII
Void SendASC(unsigned char ASC)
{
Bit es;
Es=ES;
ES=0;//Close interrupt
TI=0;
SBUF=ASC;
While(!TI);
TI=0;
ES=es;
)
//Send command to TC35
Void SendToTc35(unsigned char* p, unsigned char Long)
{
While(Long--)
{
SendASC(*p++);
}
}
// Communication interrupt receiver
Void Rs485_Do(void) interrupt 4 using 1
{
If (RI==l)
{
RI=0;
RsBuq[RsPoint++]=SBUF;
If fRsPoint" = sizeof(RsBuf))
{
RsPoint=0;//FlagRs485=0;
} //data processing
}
}
// Send AT command
Char code AT_Code[]=“OK”;
Void Send_AT(void)
{
Unsigned char *p;
While(1)
{
ClrRsBuf(RsBuf, sizeof(RsBuf));
SendToTc35(AT_Tc35,2); //"AT"
SendASC(OVER);
//************ Waiting for reply "ok"
ES=1; // must be interrupted
Delay(50);
P=strstr(RsBuf,AT_Code);
If(p!=NULL) break;
}
)
//Send bps machine command
Void Send_BPS(void)
{
SendToTc35(AT_Tc35,3); //"AT+"
SendToTc35(Bps_Tc35, sizeof(Bps_Tc35)-1); //"IPR=19200"
SendASC(OVER);
}
//Set text
Void SetText(void)
{
SendToTc35(AT_Tc35,3); //"AT+"
SendToTc35(Text_tc35, sizeof(Text_tc35)-1);//IPR=19200"
SendASC(OVER);
Delay(100):
//Delete SMS
Unsigned char EraseMsg(unsigned char index)
{
Unsigned char *p,i=20;
SendToTc35(AT_Tc35,3); //"AT+"
SendToTc35(Erase_Tc35, sizeof(Erase_Tc35)-1);//IPR=19200"
SendASC(index);
SendASC(OVER);
ES=1;
While(i--)
{
Delay(200);
P=strstr(RsBuf,AT_Code);
If(P!=NULL) {return 1;}
}
Return 0;
}
//Read SMS
Char code Ask_No[]=”+CMGR:0,,0”;
Char code ERROR{]=”ERROR”;
Char code Ask_Tc35[]=”/“;
Unsigned char ReadMsg(unsigned char index)
{
Unsigned char *p,i;
Unsigned char Buf[40];
SendToTc35(AT_Tc35,3); //"AT+"
SendToTc35(Read_Tc35,sizeof(Read_Tc35)-1);
SendASC(index);
SendASC(OVER);
ES=1; // must be interrupted
Delay(600);
/*-------
ES=0:
SendToTc35(RsBuf,99);
ES=1;
*/|
p=strstr(RsBuf,ERROR);
If(P!=NULL)
{
Send_AT();return 0;
p=strstr(RsBuf,Ask_No);//No information
If(p!=NULL)return 0;
p=strstr(RsBuf,Ask_Tc35);//20 bytes after MSG
If(p==NULL) return 0;
p=p+21;
For(i=0;i<<sizeof(Buf);i++)
{
Buf[i]=*p++;
}
If(EraseMsg(index)==0) return 0;
p=strcpy(RsBuf,Buf); //Return to RsBuf
Return 1;
)
//Send SMS
Char code SK[]=”";
Void SendMsgStart(void)
{
Unsigned char *p,i=10;
SendToTc35(AT_Tc35,3); //"AT+"
SendToTc35(Send_Tc35, sizeof(Send_Tc35)-1);//IPR=19200"
SendASC(YinHao);
SendToTc35(Mp1.Hand, sizeof(Mp1.Hand)); //"AT+"
SendASC(YinHao);
SendASC(OVER);
ES=1;
While(i--)
{
Delay(100); //Get"" "
p=strstr(RsBuf,SK);//"""
If(p!=NULL)
{
ClrRsBuf(RsBuf, sizeof(RsBuf));
Delay(150); //Get"" "
Break;
}
}
}
January 17, 2025
January 11, 2025
September 18, 2023
June 28, 2024
June 28, 2024
December 10, 2024
この仕入先にメール
January 17, 2025
January 11, 2025
September 18, 2023
June 28, 2024
June 28, 2024
December 10, 2024

Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.

Fill in more information so that we can get in touch with you faster
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.